After several approaches to junk removal, Japanese space agency JAXA, came up with the idea of a 700 meters long magnetic net, that will be sent out with a special spacecraft. The mesh of the net is made of steel and aluminum wires that collect the junk thanks to electromagnetic force. Once the net is full of debris, it de-orbits and burns up in the atmosphere.
Back in 1978 NASA scientist Donald Kessler predicted the Kessler Syndrome: collisions in space will create more and more debris that could lead to a runaway cascade and each further collision will have more debris as a result. Eventually we won't be able to leave the surface of our Earth without the risk of being smashed.
According to NASA, there are 20.000 pieces of larger orbital junk in the low Earth orbit (LEO) and 500.000 marble-sized untraceable pieces. The satellite collisions of 2009, that created huge amounts of orbital junk waste, is not the only cause. We have to think about a solution; otherwise the problem will get worse.
Via JAXA:
"EDT (Electrodynamic tether) system planned by ISTA consists mainly of a conductive bare tether and an end-mass with an electron emitter(FEAC). An electromotive force (EMF) is set up with in the conductive tether deployed from a rocket upper stage. Near-Earth space is filled with very thin plasma consisting of cations (electrically positive) and electrons (negative), and the electrons are collected through the surface of the bare tether (without insulation). On the other hand, the electrons are emitted to space through FEAC, and thus electric current flows through the tether. This current generates a Lorentz force in the opposite direction to the orbital motion. The force causes the orbital energy to decrease, resulting in lowering orbit.
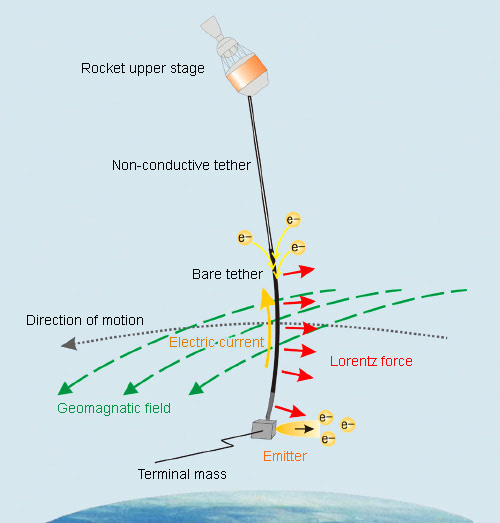
(Mission manager) Nakajima explains, "What we are studying is a debris removal vehicle with multiple EDT systems. The vehicle approaches a debris and installs one EDT system on it. The EDT system activates itself in a prescribed sequence and deploys the tether. The orbit of the debris can be lowered by the EDT thrust, until it reenters atmosphere." At present, the trial fabrications are promoted of prototype field-emission type electron sources (FEAC) using carbon nanotubes based on nanotechnology, and a conductive bare(electrically no-insulated) tethers, toward an on-orbit demonstration of EDT system aboard an rocket upper stage."
If JAXA's method will be successful, the company will increase the length of the net by 10 kilometers. Hopefully we will solve the problem, otherwise it will affect our opportunities to explore the outer space — and that would be a pity.
Source: Extreme Tech
Related Post: In Space, Nobody Can See You Litter

Share your thoughts and join the technology debate!
Be the first to comment