Biomaterials researchers at MIT came up with a very tiny device able to monitor vital signs from deep inside the body. It seems a NANO Supermarket speculative product, actually it is a new type of sensor, designed to be ingested by the patient. This invention will make it possible in the near future to monitor the heart rate and breathing from within the gastrointestinal tract.
The device is the work of Giovanni Traverso, team member at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, United States. This type of sensor could provide medical monitoring of patients with certain chronic diseases, improve the training of professional and amateur athletes, and even monitor the vital signs of soldiers on the battlefield. Since pigs' body structure is very similar to the human one, they first tested it on six sedated Yorkshire pigs. Doctors currently measure vital signs such as heart rate and breathing using techniques that include the electrocardiogram (ECG) and pulse oximetry, which require contact with the patient's skin. These vital signs can also be measured with monitoring devices that can be attached to the body, giving freedom of movement to the subjects but often these devices are uncomfortable. 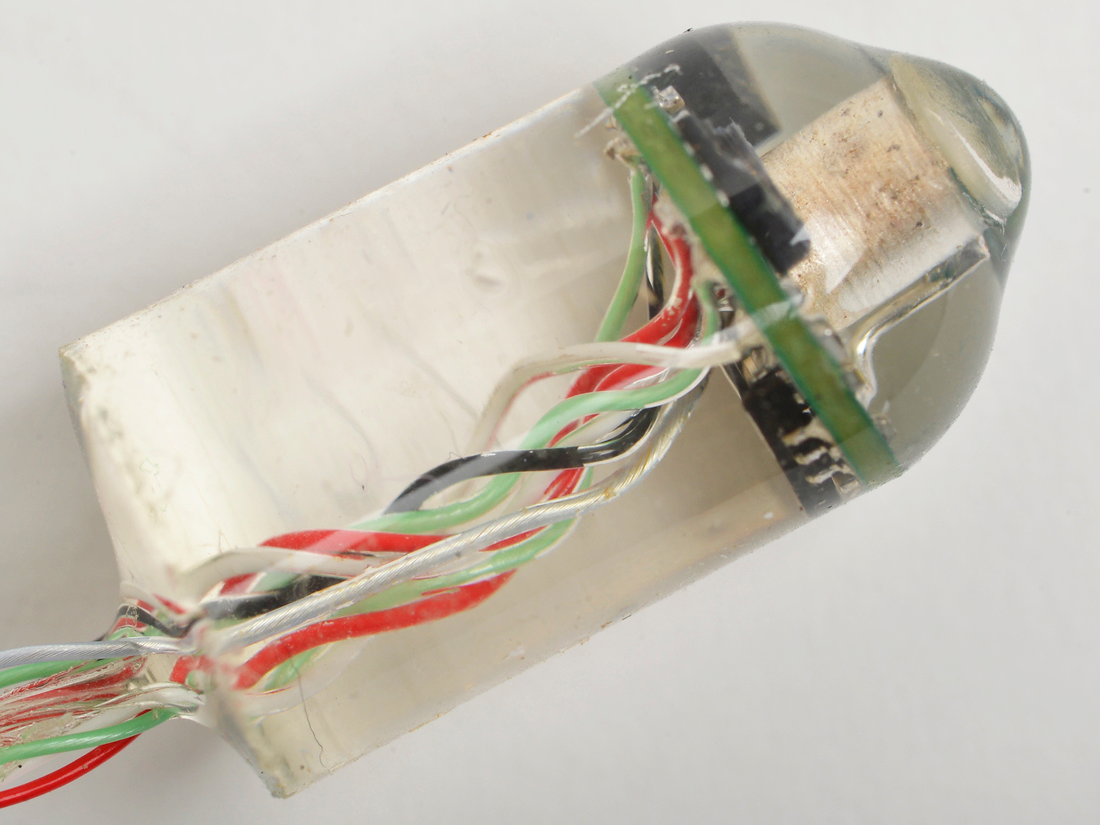 Inspired by existing ingestible devices to measure body temperature, and other internal images that capture the digestive tract, the researchers designed a sensor that measures the heart rate, breathing and temperature, from within the digestive tract. The difference between the previous methods and this one is simple. This new Nanotechnology allows them to monitor all at once, thanks to a microphone, a battery and a thermometer.
Inspired by existing ingestible devices to measure body temperature, and other internal images that capture the digestive tract, the researchers designed a sensor that measures the heart rate, breathing and temperature, from within the digestive tract. The difference between the previous methods and this one is simple. This new Nanotechnology allows them to monitor all at once, thanks to a microphone, a battery and a thermometer.
“Through characterization of the acoustic wave, recorded from different parts of the GI tract, we found that we could measure both heart rate and respiratory rate with good accuracy,” said gastroenterologist and co-lead author of the study published in PLoS One Giovanni Traverso. “We hope that one day we’re able to detect certain molecules or a pathogen and then deliver an antibiotic, for example. This development provides the foundation for that kind of system down the line”.
Source: MIT. Image: Shutterstock

Share your thoughts and join the technology debate!
Be the first to comment